Your Tesla sits silent in the driveway. The touchscreen remains dark, the doors won’t respond to your key fob, and you’re unexpectedly stranded. While Teslas don’t require traditional jump starts for their main drive battery, their smaller 12V auxiliary battery can fail—leaving you unable to access your vehicle or activate its systems. Understanding how to properly address this situation with a portable jump starter is crucial, but safety must come first. Unlike conventional vehicles, Tesla’s electrical architecture requires specific procedures that differ significantly from standard jump-start methods.
Here’s what’s critically important to know: Tesla does not officially endorse or provide jump-start procedures using third-party portable jump starters in their current documentation. When the 12V battery fails, you’re not jump-starting the main power system but attempting to provide enough power to the auxiliary system to wake up the vehicle’s computers. This distinction matters because improper procedures could damage sensitive electronics or create safety hazards. As you search for solutions, you need accurate, manufacturer-verified information—not unconfirmed online advice that could put you at risk.
Why Reliable Information Is Critical for Tesla 12V Issues
Tesla’s electrical systems operate differently than traditional vehicles, making accurate guidance essential. The 12V battery in a Tesla powers critical systems including door locks, computers, and the contactors that connect the main high-voltage battery. When this auxiliary battery fails, the vehicle becomes unresponsive. However, unlike gasoline cars where jump-start procedures are standardized, Tesla’s approach to 12V recovery has evolved significantly across models and software versions.
Recent Tesla service documentation indicates the company has moved away from recommending traditional jump-start methods altogether. Instead, Tesla’s official guidance now emphasizes using their mobile service or roadside assistance when 12V battery issues occur. This shift reflects the complexity of modern Tesla electrical systems where improper jump-start attempts could potentially damage the vehicle’s power electronics or create safety hazards near high-voltage components.
Without verified procedures from Tesla, attempting to jump-start your vehicle could lead to serious consequences including electrical system damage, voided warranties, or personal injury. The absence of official documentation for this specific procedure should be treated as a significant warning—not as an opportunity to improvise with potentially dangerous methods.
Official Tesla Resources for 12V Battery Issues
Tesla Roadside Assistance Protocol
When your Tesla won’t power on due to suspected 12V battery failure, your safest option is contacting Tesla Roadside Assistance at 1-877-798-3752. Their technicians follow manufacturer-approved protocols that have been tested across all Tesla models and software versions. Modern Tesla vehicles often include built-in diagnostics that communicate directly with roadside assistance, allowing them to determine whether the issue requires a simple reset, a temporary power solution, or full battery replacement.
Tesla Roadside Assistance is included for four years or 50,000 miles on new vehicles, making this the most reliable and risk-free solution. Their technicians arrive equipped with specialized tools and knowledge of the latest procedures for your specific model year and software version—something no generic jump starter guide can provide.
Mobile Service Replacement Procedure
In most cases, when a Tesla 12V battery fails completely, replacement is necessary rather than temporary jump-starting. Tesla’s mobile service technicians can typically replace the 12V battery at your location in under 30 minutes. This service is significantly more efficient and safer than attempting to jump-start the system yourself, as it addresses the root cause rather than providing a temporary workaround.
The process involves:
1. Diagnosing whether the 12V battery failure is isolated or indicative of other electrical issues
2. Safely accessing the 12V battery compartment using model-specific procedures
3. Installing a manufacturer-approved replacement battery
4. Performing system diagnostics to ensure proper operation
Safe Alternatives When Assistance Isn’t Immediately Available

Using Your Mobile Connector as Emergency Power
If you have your Tesla Mobile Connector (the standard charging cable that comes with the vehicle), this can sometimes provide enough power to wake up the 12V system. Plug the connector into a standard 120V household outlet and connect it to your Tesla’s charge port. In many cases, this provides sufficient power to:
- Unlock the doors
- Activate the touchscreen
- Allow normal startup procedures
This method is safer than attempting traditional jump-start procedures because it works within Tesla’s designed electrical architecture rather than bypassing it. The Mobile Connector delivers power through the vehicle’s intended charging circuitry, which includes necessary safety protocols and voltage regulation.
Emergency Access Procedures
All Tesla models include mechanical emergency access methods that don’t require 12V power:
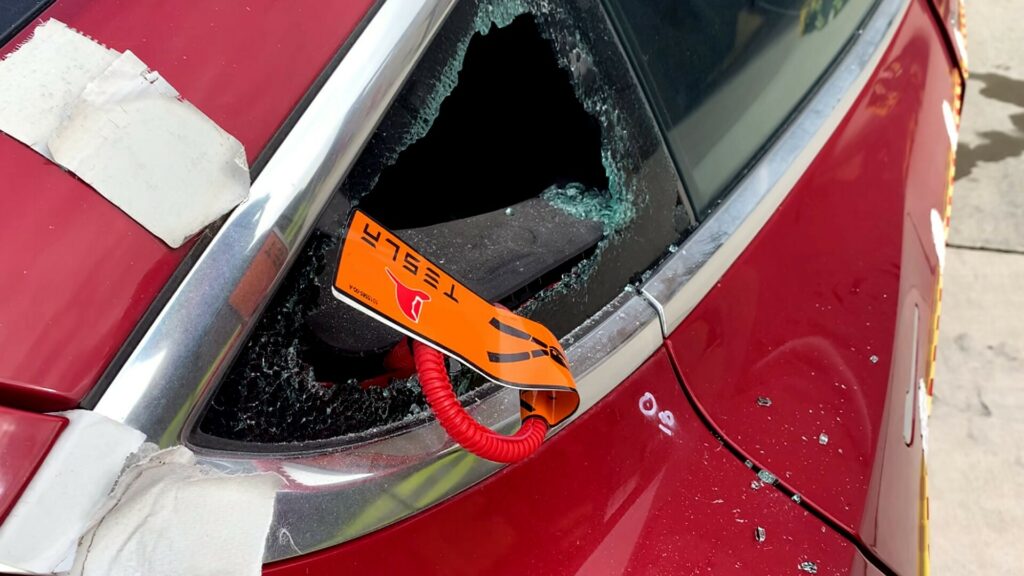
Model 3 and Model Y:
– Locate the small release tab beneath the touchscreen area (visible when the screen is off)
– Pull this tab to manually release the driver’s door
Model S and Model X:
– Use the physical key blade stored in your key fob
– Insert into the door handle’s hidden keyhole (covered by a rubber flap)
Once inside, you can access the frunk or trunk manually to retrieve your Mobile Connector if needed. These emergency access methods are documented in your owner’s manual and represent Tesla’s officially recommended approach when the 12V system fails.
Critical Safety Considerations

High-Voltage System Risks
Tesla vehicles contain extremely dangerous high-voltage components that operate at approximately 400 volts in most models. Unlike conventional vehicles, attempting to access or manipulate electrical systems without proper training puts you at serious risk of electrical shock or arc flash hazards. The orange-colored wiring throughout Tesla vehicles indicates high-voltage circuits that should never be touched during any emergency procedure.
Portable jump starters rated for conventional vehicles may not provide the stable voltage regulation Tesla’s sensitive electronics require. Voltage spikes from improper equipment could damage multiple control modules, resulting in repair costs far exceeding the price of a new 12V battery.
Why Generic Jump-Start Advice Is Dangerous
Online forums and videos often share jump-start procedures that worked on older Tesla models but may be unsafe or ineffective on current vehicles. Tesla frequently updates its electrical architecture through both hardware revisions and over-the-air software updates. A method that worked on a 2018 Model S might damage a 2023 Model Y due to differences in battery management systems.
Without access to current, model-specific service documentation—which Tesla restricts to authorized service centers—any jump-start instructions circulating online should be treated as potentially outdated or incorrect.
Proactive Prevention Strategies

Monitoring 12V Health
Your Tesla’s touchscreen provides 12V battery voltage information through the service menu:
1. Touch “Controls” on the display
2. Select “Service”
3. Choose “12V Battery Health”
Regularly checking this reading (when above 12.4V is normal, below 12.0V indicates potential issues) allows you to address problems before complete failure occurs. Unlike traditional vehicles, Teslas don’t provide gradual warning signs like slow cranking—failure is often sudden and total.
Scheduled Maintenance Approach
Rather than waiting for failure, consider replacing your Tesla’s 12V battery every 3-4 years as preventative maintenance. This simple service, which most Tesla service centers can perform in under 30 minutes, prevents the inconvenience and potential safety risks of being stranded with a dead 12V system. The cost of preventative replacement is minimal compared to potential towing fees or collateral damage from improper jump-start attempts.
When Professional Help Is Absolutely Necessary
Seek immediate Tesla service if you notice:
– Swelling or deformation of the 12V battery case
– Corrosion or leakage around battery terminals
– Burning smells from electrical components
– Error messages related to high-voltage systems
These conditions indicate potentially serious electrical issues that require professional diagnosis. Attempting DIY solutions in these scenarios could compromise your safety or result in extensive vehicle damage.
Final Note: While numerous online resources claim to provide jump-start procedures for Teslas, the absence of current, manufacturer-verified instructions makes these methods potentially risky. Tesla’s recommended approach—contacting Roadside Assistance or using your Mobile Connector for emergency power—represents the safest path forward. When your Tesla won’t power on, prioritize safety over convenience by using official Tesla support channels rather than unverified online methods that could create more serious problems. Your vehicle’s sophisticated electrical architecture deserves the expertise of trained technicians who work with these systems daily.